When bringing home a bag of bee pollen from a local beekeeper at the farmer’s market last year, I wasn’t sure exactly what to do with it. I did know (from previously listening to a podcast episode like this Realfoodolgy podcast episode with Beekeeper’s Naturals founder Carly Stein) that it can be beneficial to consume, which is why I purchased the bag in the first place. How, exactly, it was health-promoting, I wasn’t sure, so having this new bag of golden goodness from the bees led me to do a little investigation on its health benefits and ways to use it.
This bog post details what I learned about bee pollen through my research: it’s health benefits, ways to creatively use it, and the importance of responsible sourcing and caring for our essential pollinators.
Understanding Bee Pollen: A Nutrient Powerhouse
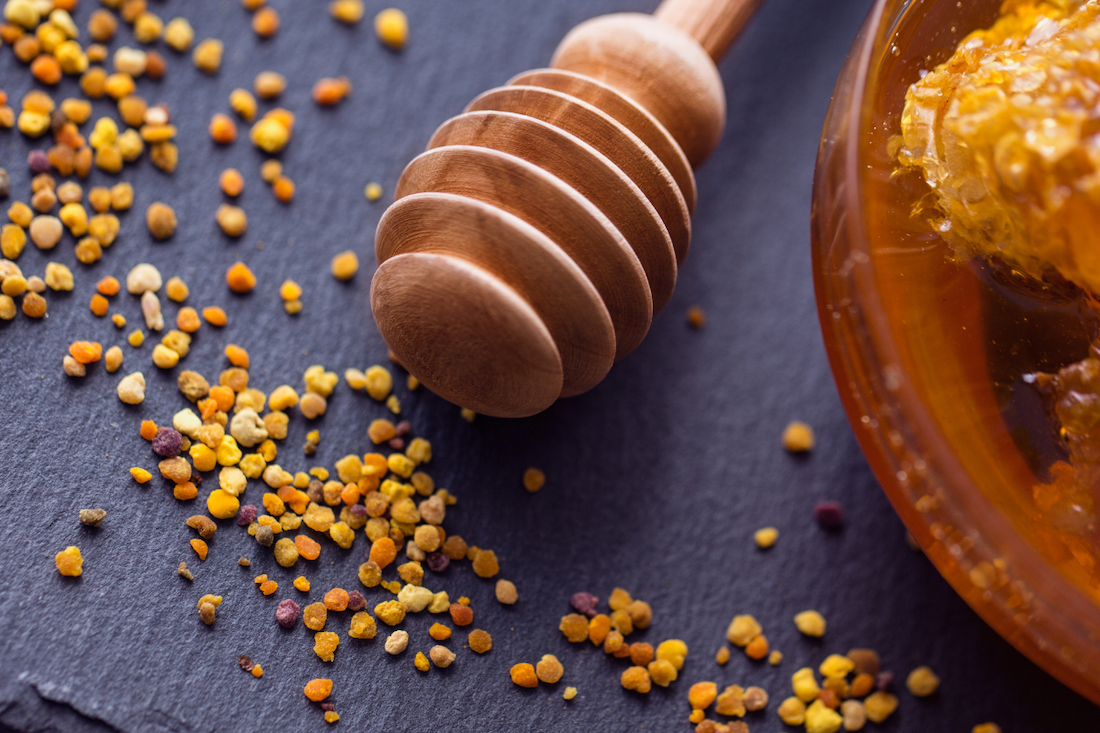
Bee pollen is the result of bees collecting pollen from flowers, mixing it with their saliva and nectar, and packing it into tiny granules. You may notice these granules attached to the legs of bees, sometimes referred to as “pollen pants” or “saddlebags.” When brought back to the hive, these golden nuggets are harvested by beekeepers (hopefully in a sustainable manner, which is discussed below). They are rich in vitamins, minerals, amino acids, antioxidants, and enzymes. The German Federal Board of Health even recognizes bee pollen as a medicine.
Health Benefits of Bee Pollen: Why It’s a Superfood
Here are some of the benefits of bee pollen.
- Supports Immunity: Bee pollen contains vitamin C among other immune-supporting nutrients. It also contains antimicrobial and antiviral properties.
- Enhances Energy Levels: Athletes often turn to bee pollen for its natural energy-boosting properties. It’s a rich source of carbohydrates and protein, offering a sustainable and natural energy source.
- Allergy Relief: Bee pollen, especially bee pollen local to your geographical area, can help alleviate seasonal allergies. By exposing your body to small amounts of the allergens found in bee pollen, you may build up tolerance over time.
- Anti-Inflammatory: Bee pollen contains anti-inflammatory compounds that might help reduce inflammation.
- Skin Health: Bee pollen contains antioxidants, helping the body to combat free radicals, potentially slowing down the aging process and promoting healthy skin.
- Digestive Aid: Bee pollen contains enzymes that may support digestion, promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
Creative Ways to Use Bee Pollen:
Here are some ways to incorporate bee pollen into a daily routine:
- Sprinkle on yogurt
- Add to smoothies
- Stir into oatmeal
- Sprinkle on cereal
- Sprinkle on muffins
- Sprinkle on pancakes or waffles
- Add to no-bake energy balls
- Mix with honey to spread on toast or to sweeten tea
- Top salads
- Add to guacamole
- Add to homemade smoothie popsicles
- Sprinkle on top of ice cream (like this healthy homemade ice cream)
- Sprinkle on dark chocolate bark for a sweet treat
It is important to note that, although bee pollen is generally safe and beneficial for use, it can cause an allergic reaction in some people, so it’s recommended to start out trying just a small amount to begin with. Also, consult with your health care provider if you are pregnant or on medications such as blood thinners.
How to Store Bee Pollen:
Bee pollen, when stored under the right conditions, can remain edible and retain its nutritional value for an extended period. It can typically last for one to two years without significant deterioration if stored correctly.
To ensure bee pollen stays fresh, it’s essential to store it properly:
- Cool and Dry Environment: Keep bee pollen in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Exposure to heat and moisture can lead to spoilage.
- Airtight Container: Store bee pollen in an airtight container to prevent exposure to air, which can cause it to lose flavor and nutritional potency.
- Refrigeration: Storing bee pollen in the refrigerator can extend its shelf life, especially if you live in a warm and humid climate.
Responsible Sourcing: Protecting Our Pollinators
When first purchasing and trying bee pollen, I couldn’t help but wonder if my decision had a negative impact on the bees. They work hard to collect pollen and make these compacted granules, so surely they need them, right? Yes, they do. Bees collect pollen as a primary source of protein for their colonies. When beekeepers harvest pollen, it reduces the bees’ food reserves. This can potentially stress the hive, especially during periods of low forage availability, like fall and winter. To mitigate this, responsible beekeepers ensure that they leave enough pollen for the bees’ needs. So, it is crucial to be mindful of some important considerations:
- Support Responsible Beekeepers: When purchasing bee pollen, opt for sources that prioritize the health and welfare of bee colonies. Responsible beekeepers follow ethical practices and ensure that their bees have sufficient food reserves.
- Sustainable Harvesting: Beekeepers should use sustainable and non-invasive methods for collecting pollen to minimize stress on the bees. This includes using well-designed pollen traps and timing collections to minimize disruptions.
- Avoid Pesticide Exposure: Choose bee pollen from areas with minimal pesticide use. Pesticides can harm bee populations and contaminate their products.
- Bee Health Management: Responsible beekeepers regularly inspect their hives and manage diseases and pests to maintain strong, healthy bee colonies.
Some more fun facts about bee pollen:
- Bee Pollen is a Complete Protein Source: Bee pollen is considered one of nature’s most complete foods because it contains all the essential amino acids required by the human body.
- Colorful and Varied: Bee pollen comes in a wide range of colors, including yellow, orange, red, and green, depending on the types of flowers visited by the bees.
- Nutrient-Dense: Bee pollen is packed with nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and antioxidants, making it a true superfood.
- Diverse Floral Sources: Bees collect pollen from various plants, which means that bee pollen can vary significantly in composition and flavor based on the local flora.
- Long History of Use: Bee pollen has been used for its health benefits for centuries, with historical records dating back to ancient Egypt.
With its many benefits and versatile uses, bee pollen can be a great addition to a wellness routine. Before supplementing with bee pollen, as with any new supplementation regimen, it is recommended to check with your healthcare provider first, especially if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking medications. Also, it is vital to remember that our pollinators, the bees, play a crucial role in our ecosystem. By supporting responsible sourcing and ethical beekeeping practices, we can ensure that we continue to enjoy the gifts of nature while protecting the bees that make it all possible. 🐝🌼
Sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8230257/
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/bee-pollen#TOC_TITLE_HDR_2
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4276980/